Muscle oxygen sensors have grown in popularity as a tool for athletes and coaches looking to improve their training and performance. These sensors determine the oxygen saturation levels in the muscles, providing significant information about training effectiveness and recovery. However, not all muscles are made equal, and some are better suited than others for measurement with muscle oxygen sensors. In this post, we'll talk about which muscles are excellent for measuring using muscle oxygen sensors and in what kind of exercise or sport.
Measuring muscle oxygen in the lower body
Quadriceps
The quadriceps are one of the largest muscle groups in the body, responsible for powering movements such as squats, lunges, and jumps. Measuring the oxygen saturation levels in the quadriceps can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of lower body workouts, such as leg day at the gym or endurance activities such as running and cycling.
Hamstrings
The hamstrings are located on the posterior of the thighs and are responsible for extending the hip and bending the knee. Measuring the oxygen saturation levels in the hamstrings can help optimize training for sports that require explosive movements, such as sprinting or jumping.
Calf Muscles
The calf muscles are responsible for plantarflexion, which is the movement of pointing the toes downward. Measuring the oxygen saturation levels in the calf muscles can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of exercises such as calf raises or running.

Measuring muscle oxygen in the upper body
Forearms
When it comes to training, the forearms are often overlooked, although they play an important part in several sports, including tennis, basketball, and golf but also in grip strength, essential for several strength exercises. Measuring oxygen saturation levels in the forearms can help optimize training and prevent injuries in various sports.
Trapezius
The trapezius muscle is located in the upper back and is responsible for shoulder movement and neck stabilization. Measuring the oxygen saturation levels in the trapezius muscle can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of upper body workouts, such as shoulder presses or pull-ups.
Quick tip: Did you know you do not need to use the strap to place the sensor on your body? Especially for muscles like the m. trapezius where a strap will be impacting your performance, the Train.Red Patch is a targeted solution.
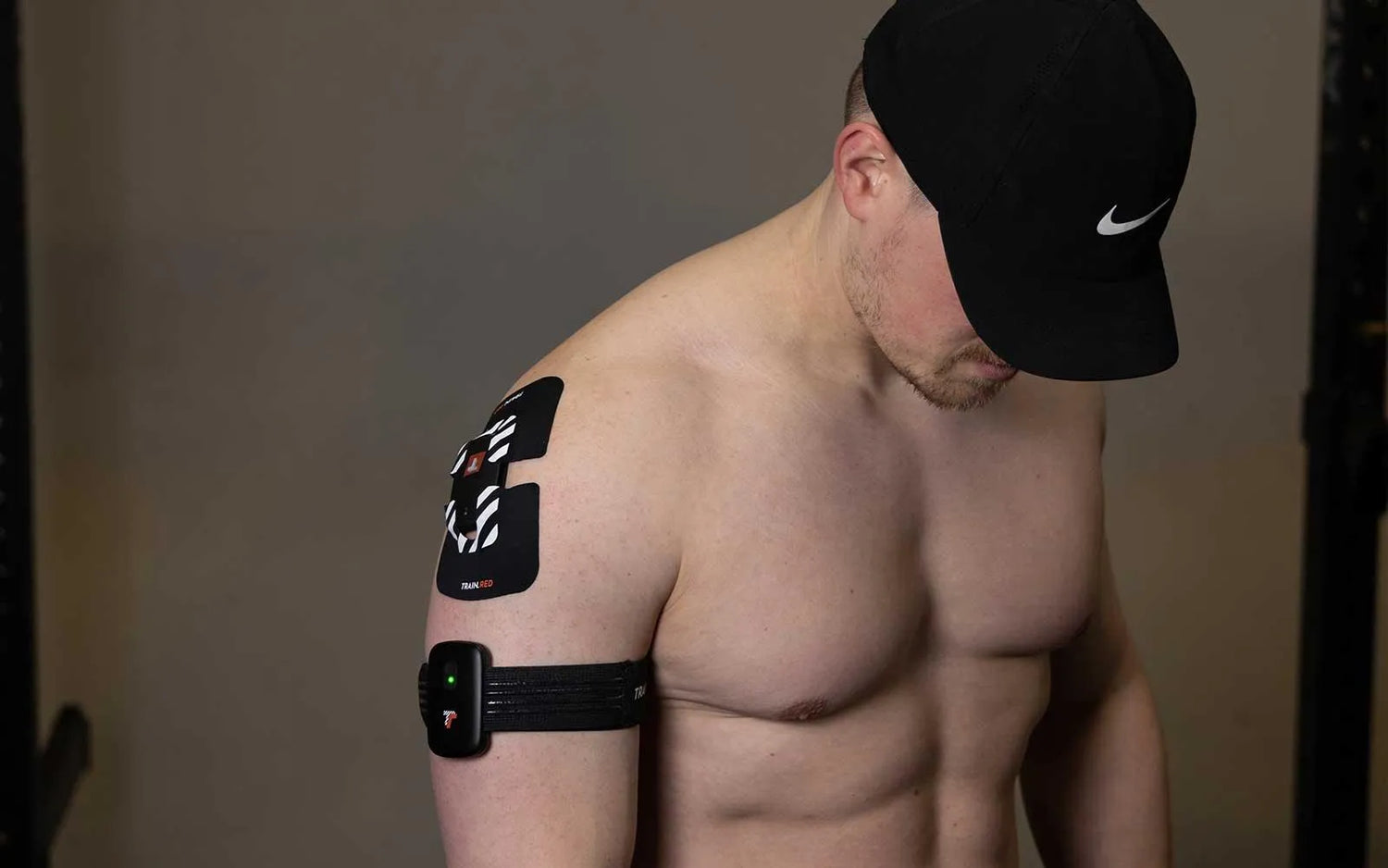
Biceps
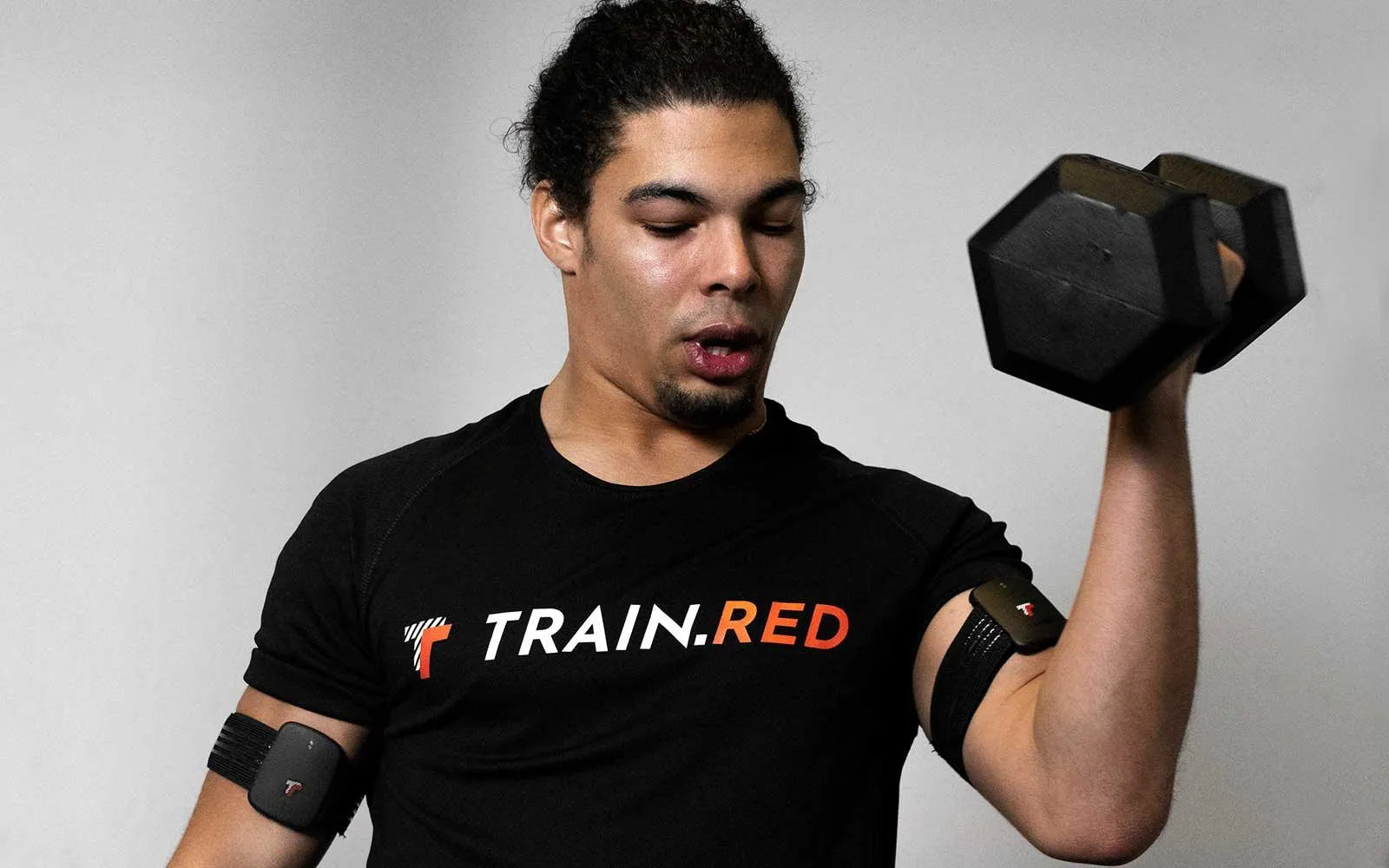
The biceps are the muscles in the front of the upper arms that control elbow flexion. Measuring oxygen saturation levels in the biceps can help optimize training for upper-body strength sports like weightlifting or boxing and are used in several strenght exercises.
Triceps
The triceps muscles are placed in the rear of the upper arms and are in charge of elbow extension. Measuring oxygen saturation levels in the triceps can provide useful information about the effectiveness of activities like push-ups and bench press.
Lats
The latissimus dorsi, or lats for short, are located in the middle of the back and are responsible for movements such as pulling or rowing. Measuring the oxygen saturation levels in the lats can help optimize training for sports that require upper body strength and endurance, such as swimming or rowing.

Conclusion
Muscle oxygen sensors can help athletes and coaches improve their training and performance. Athletes can receive useful insights into the effectiveness of their workouts and make adjustments to their training plan by measuring the oxygen saturation levels in individual muscles. Depending on the sort of exercise or sport, the quadriceps, hamstrings, calf muscles, forearms, biceps, triceps, lats, and trapezius are all excellent muscles to monitor with muscle oxygen sensors. So, the next time you train, think about evaluating the oxygen saturation levels in these muscles to improve your performance.
If you’re looking to purchase a device, go to our shop or plan a free demo call to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can muscle oxygen sensors be used for all types of sports?
A: Yes, muscle oxygen sensors can be used for all types of sports that involve muscle movement.
Q: Are muscle oxygen sensors accurate?
A: Yes, muscle oxygen sensors are highly accurate and provide real-time data on oxygen saturation levels in the muscles.
Q: How often should muscle oxygen sensors be used during training?
A: The frequency of using muscle oxygen sensors can vary depending on the athlete's goals and training regimen. However, it's recommended to use them regularly during training to track progress and make adjustments to the training plan.
Q: Can muscle oxygen sensors help prevent injuries?
A: Yes, by measuring the oxygen saturation levels in specific muscles, muscle oxygen sensors can help athletes prevent injuries by identifying imbalances or weaknesses in their training.
Q: Are muscle oxygen sensors easy to use?
A: Yes, muscle oxygen sensors are user-friendly and easy to use, with many options available for both professional athletes and amateur fitness enthusiasts.